14 Event based surveillance
How do we find public health threats that we did not anticipate?
Warning: This is not ready
Event based surveillance is a defined system that rapidly detects events that might be a threat to public health. These events could be news reports, rumors, social media or informations by other surveillance systems. The collected events are then analysed, assessed and the relevent information is disseminated. The goal of an event based surveillance system is to provide an early warning system and detect previously unkown or generally threats, that are not detected by indicator based surveillance systems.
14.1 Stages of event based surveillance
14.2 Terminology
14.2.1 Event based vs. indicator based surveillance
The termin indicator based surveillance is opposite to event based surveillance. Indicator based means that there are predifined indicators that are monitored, for example a syndromic or case-based surveillance system. When you look closely the line becomes somwhat blurred because event based surveillance can also incooperate indicator based surveillance.
| Characteristic | Indicator based surveillance | Event based surveillance |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Routine, Systematic, Pre-defined pathways and indicators | Formalized, Ad hoc and in real time, Flexible |
| Data | Organized data with predefined variables, Trusted and reliable, often health-care sector based | Not organized or predefined (variable), Reliability to be assessed |
| Sources | Formal sources (usually one sector) | All sources (Meida/Internet, Communication, Indicator based surveillance) |
14.2.2 Epidemic intelligence
Event based surveillance and epidemic intelligence are often used as synonyms. But some argue that epidemic intelligence is broader than event based surveillance to emphasize the fact that it also uses indicator based surveillance and encompasses the verification, assessment and investigation steps1. But as the usage of indicator based surveillance and steps of verification, assessment and investigation also falls within the definition of event based surveillance or surveillance in general, there is no need to use the term epidemic intelligence.
14.3 Strengths and weaknesses
Strengths:
- Can detect unkown or not-thought of public health threats - Is usually fast - Has a formalised way of assessing risks
Weakness: - Large subjective component - Does not give reliable statistical measurements (e.g. trends)
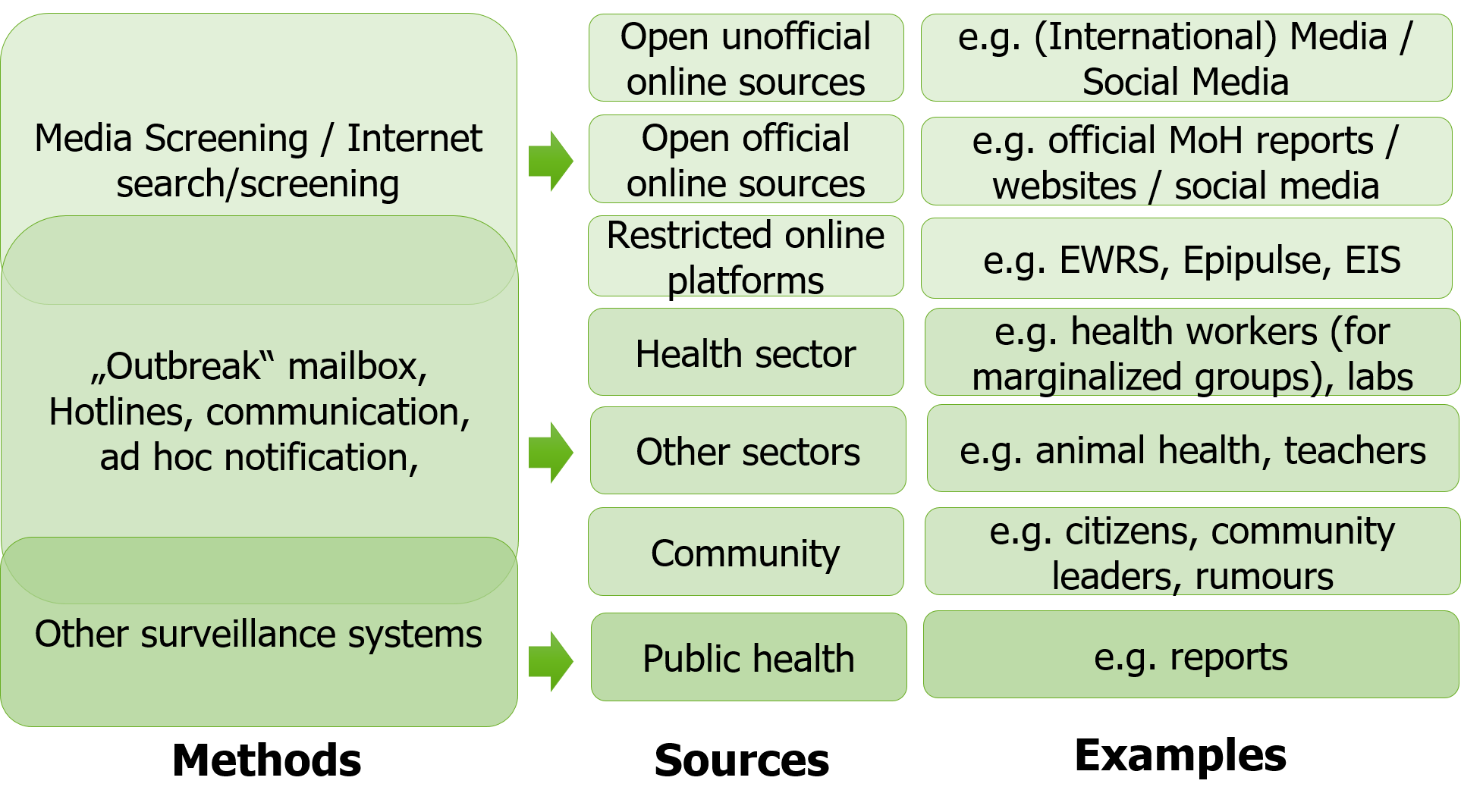
14.4 Sources of event based surveillance
14.5
An example of such surveillance is an expert commission that regularly meets to collect potentially relevant events.